Contracts are an integral part of any business transaction or relationship. They help to set out the expectations and obligations of all parties involved, as well as provide a legal framework for resolving disputes if they arise. One important aspect of contracts is the inclusion of specific clauses that outline the contractual provisions, terms and conditions of the agreement. One such clause is the contract clause. In this article, we will define what is a clause in a contract, the types of contracts clause, and their importance.
Also Read: Contract Administration vs Contract Management
What is Contract Clause Definition?
A contract clause is a provision or section of a contract that sets out specific terms and conditions that the parties agree to abide by. Contract clauses can cover a wide range of topics, from payment terms and delivery schedules to warranties, liability, and termination rights. In essence, they provide a detailed roadmap of what each party is agreeing to do and not do under the terms of the contract.
Also Read: Signature guarantee vs notary
Common Contract Clauses
Below is the list of common types of clauses in a contract:
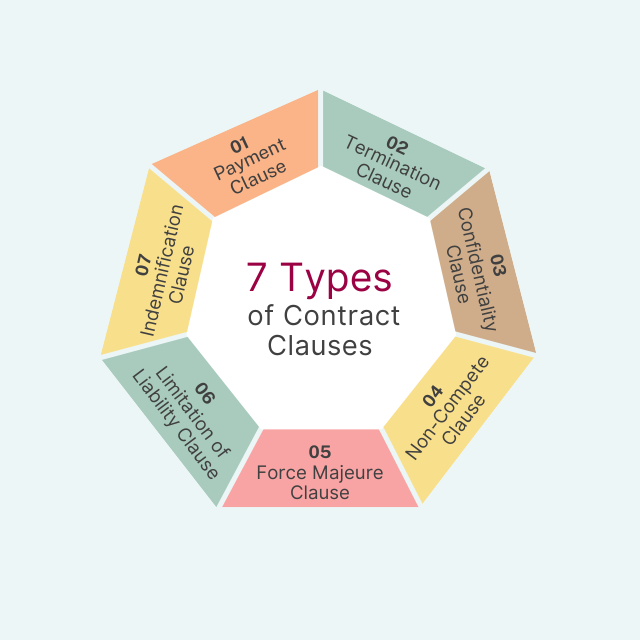
1. Payment Clauses
The payment clause of a contract specifies the payment terms for the goods or services provided under the contract. Payment clauses may include the amount of payment, the currency in which payment will be made, the timing of payment, and any penalties for late payment.
Also Read: What is CLM
2. Termination Clauses
The termination clause in contract specifies the circumstances under which the contract can be terminated by either party. They may also set out the notice period required for termination and any penalties or damages that may apply if the contract is terminated.
Also Read: What can contract management software ensure
3. Confidentiality Clauses
Confidentiality clauses are often included in contract provisions that involve the exchange of confidential information between the parties. These contractual clauses set out the obligations of each party to keep the information confidential and prohibit the use or disclosure of the information to third parties.
Also Read: How to write a contract proposal
4. Non-Compete Clauses
Noncompete clauses in contracts are often used in employment contracts to prevent employees from working for a competitor for a certain period after leaving their current employer. A non-compete clause in contract may also be included between businesses to prevent one party from competing with the other for a certain period.
Also Read: Adding an addendum to a contract
5. Force Majeure Clauses
Force majeure clauses are used to excuse a party from performing its obligations under the contract if events beyond its control occur, such as natural disasters, war, or strikes. These agreement clauses typically specify the types of events that will trigger the clause and the obligations of the parties during the force majeure event.
Also Read: Contract lifecycle management blockchain
6. Limitation of Liability Clauses
Limitation of liability clauses limit the liability of one or both parties under the contract. These clauses may limit the types of damages that can be claimed, the amount of damages that can be claimed, or both.
Also Read: Definition of implied contract
7. Indemnification Clauses
Indemnification clauses require one party to compensate the other for any losses, damages, or expenses that arise as a result of the other party’s actions or omissions. These clauses can be unilateral, with one party indemnifying the other, or mutual, with both parties agreeing to indemnify each other.
Also Read: How to get an affidavit notarized
Contract Clause Purpose Explained
A clause specifies the provisions of the contract and the circumstances under which it may be enforced in court. Contracts frequently include boilerplate language or generic language that appears in all contracts. There isn’t much wiggle room in these typical clauses. Contracts may occasionally include very detailed language that is related to a particular situation or aspect of the agreement.
Contract clauses are crucial for defining the specific circumstances in which parties agree to the terms of the agreement. Additionally, they can offer guidance on how the contract will be enforced in certain scenarios. For instance, if your employment contract included language requiring employees to maintain the privacy of company information, they would have to do so.
Also Read: Can I notarize for a family member in NY
What is the Importance of Clause in a Contract?
Clarity: Contract or agreement clauses help to provide clarity and avoid misunderstandings between the parties. By specifying the obligations of each party, the parties can ensure that they are on the same page regarding what is expected of them under the contract.
Risk Allocation: Contract clauses can help to allocate risk between the parties. For example, a limitation of liability clause may limit the liability of one party in the event of a breach of contract, reducing the financial risk for that party.
Legal Protection: Contract clauses provide legal protection for the parties in the event of a dispute. By setting out the terms of the agreement in writing, the parties have a clear record of their intentions and obligations under the contract, which can be used as evidence in court if necessary.
Managing Expectations: Contract clauses can help to manage the expectations of the parties involved. By setting out the terms of the agreement in detail, each party can have a clear understanding of what they are getting into and what they can expect from the other party.
Compliance: Contract clauses can ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. For example, contracts in certain industries may be subject to specific laws or regulations, and legal clauses can be included to ensure compliance with these requirements.
Relationships: Contract clauses can also help to manage the relationship between the parties. By setting out the obligations and expectations of each party, the contract can help to build trust and strengthen the relationship between the parties.
Enforcement: Contract clauses can help to ensure that the terms of the contract are enforced. By setting out the consequences of a breach of contract, parties can be incentivized to adhere to the terms of the agreement.
Efficiency: Contract clauses can help to streamline the negotiation and drafting process. By setting out common contract clauses in advance, parties can save time and money by avoiding lengthy negotiations and discussions on standard terms.
Communication: Contract clauses can promote effective communication between the parties. By setting out expectations and obligations in writing, parties can avoid misunderstandings and ensure that both parties are on the same page.
>>>Download and use free contract templates from Legitt
Conclusion
Overall, contract clauses are essential for any business relationship or transaction. They help to manage expectations, allocate risk, provide legal protection, and promote effective communication and relationships between the parties. While it may be tempting to skip over the fine print, the devil is truly in the details, and paying attention to contract clauses can prevent a lot of headaches down the road.
Did you find this Legitt article worthwhile? More engaging blogs about smart contracts on the blockchain, contract management software and electronic signatures can be found in the Legitt Blogs section. You may also contact Legitt to hire the best contract lifecycle management services and solutions.
FAQs on Contract Clause
What is a clause in legal terms?
In legal terms, a clause refers to a distinct provision or section within a legal document or contract that addresses a particular issue or topic, and which has its own unique meaning and interpretation.
What is the difference between contract clause and provision?
In legal terms, a contract clause and a provision are often used interchangeably to refer to a distinct section within a legal document that sets out a specific term or condition. However, a provision may refer more broadly to any part of a legal document, while a clause typically refers to a specific provision addressing a particular issue or topic.
Why do we need clauses in a contract?
Clauses are needed in a contract to set out the terms and conditions of the agreement between the parties involved, including defining their respective rights and obligations, allocating risks and responsibilities, and providing legal protection in case of disputes or breaches.
What are the main clauses of the contract?
The main clauses of a contract can vary depending on the specific terms of the agreement, but typically include clauses related to the parties' identities, the scope of the agreement, the obligations and responsibilities of each party, payment terms, confidentiality and non-disclosure, dispute resolution, and termination.
Can clauses in a contract be changed or modified after it has been signed?
Clauses in a contract can be changed or modified after it has been signed, but only with the agreement of all parties involved and with proper documentation, such as an amendment or addendum to the original contract.
How do clauses in a contract differ from the terms and conditions?
Clauses in a contract are specific provisions or sections that address particular issues or topics within the agreement, while the terms and conditions refer more broadly to the overall provisions, requirements, and obligations set out in the contract, including the clauses themselves.
Can a clause in a contract be deemed unenforceable?
Yes, a clause in a contract can be deemed unenforceable if it is found to be illegal, against public policy, or unconscionable. Additionally, a court may interpret a clause in a way that renders it unenforceable based on the specific circumstances of the case.
How do you ensure that all necessary clauses are included in a contract?
To ensure that all necessary clauses are included in a contract, parties should carefully review the terms of the agreement and consider consulting with legal professionals to ensure that all relevant issues and concerns are addressed in the contract and that it reflects their intended understanding and expectations.





















